Xanthelasma
Xanthelasma
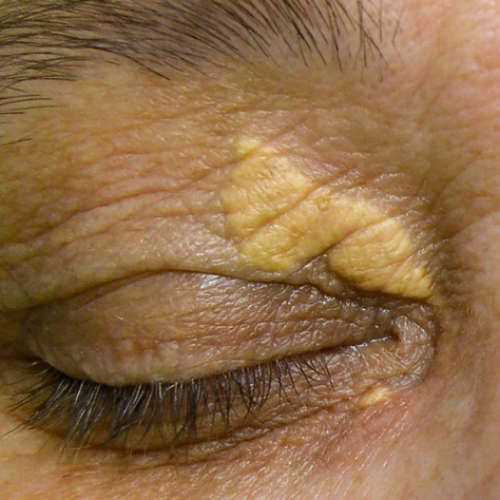
Xanthelasma is a skin condition characterized by yellow, puffy patches that typically appear on the corners of the eyelids. These patches are caused by the accumulation of fatty cholesterol deposits beneath the skin. While xanthelasma is generally asymptomatic and not painful, it can signal underlying lipid imbalances, such as elevated cholesterol levels. Often seen in middle-aged individuals, particularly women, xanthelasma can be a cosmetic concern due to its prominent location around the eyes and its noticeable yellow color.
High Cholesterol Levels: The most common cause of xanthelasma is elevated cholesterol levels in the blood, particularly high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), also known as “bad” cholesterol. When there is excess cholesterol in the blood, it can accumulate in the skin, leading to the formation of yellow plaques.
Genetic Factors: Genetics can play a significant role in the development of xanthelasma. People with a family history of high cholesterol or xanthelasma are at a higher risk of developing the condition. In some cases, xanthelasma can be inherited as part of a genetic disorder called familial hypercholesterolemia.
Age and Gender: Xanthelasma is more common in middle-aged or older adults and is particularly prevalent in women, possibly due to hormonal changes that affect cholesterol levels. It typically develops after the age of 40, although it can occur at any age.
Diabetes: People with diabetes, particularly those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels, are more prone to developing high cholesterol and xanthelasma. Liver disease: Conditions like cirrhosis or fatty liver disease can disrupt cholesterol metabolism, leading to the development of xanthelasma.
Hypothyroidism: Low thyroid hormone levels can also contribute to high cholesterol levels, increasing the likelihood of xanthelasma formation.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a known risk factor for high cholesterol, which can contribute to the formation of xanthelasma. Fatty deposits in the body may also lead to an imbalance in cholesterol metabolism.
Redness and Swelling : Common after procedures like laser therapy, cryotherapy, or chemical peels.Typically temporary and resolves within days.
Scabbing or Crusting:May develop as the skin heals after treatment. A normal part of the recovery process.
Slight Bleeding or Oozing:Possible with surgical excision or ablative treatments.
Pigmentation Changes: Hyperpigmentation (dark spots) or hypopigmentation (light spots) may occur, especially in darker skin tones. Often temporary but can be permanent in rare cases.
Itching or Irritation : Mild discomfort as the skin heals after the procedure.
Tenderness or Sensitivity:Treated areas may feel tender to touch.Sensitivity to sunlight is common, requiring sun protection.
Improved Aesthetic Appearance: One of the main reasons people seek treatment for xanthelasma is to improve their appearance. Removing the yellowish plaques can restore a more youthful and smooth look to the eyelids and surrounding skin, boosting confidence and self-esteem.
Prevention of Growth and Spread: Xanthelasma can grow over time and may even spread to other areas of the face or body. Treatment can help prevent further growth or the appearance of additional plaques, keeping the condition from becoming more prominent.
Potential to Address Underlying Health Issues: While xanthelasma itself is not harmful, its presence can indicate high cholesterol or lipid imbalances in the body. Treatment may prompt individuals to seek a medical evaluation for cholesterol and lipid levels.
Non-invasive Treatment Options: There are non-invasive or minimally invasive treatment options available for xanthelasma, such as laser therapy, cryotherapy (freezing), or chemical peels. These treatments generally involve little to no downtime, allowing individuals to resume normal activities quickly.
Quick and Effective Results: Treatments for xanthelasma are generally quick, with many patients seeing visible improvements after just one or a few sessions. Laser treatment, for example, can effectively target the plaques and reduce their appearance without damaging surrounding skin.
Frequently Ask Question
- Xanthelasma is a condition characterized by yellowish, soft, and painless plaques that typically appear on or around the eyelids. They are made up of cholesterol deposits and are common in adults, especially those with high cholesterol or lipid imbalances.
Xanthelasma is generally harmless and not a medical emergency. It is a benign condition that does not cause pain or discomfort. However, it can be a cosmetic concern for many individuals.
The primary cause of xanthelasma is the accumulation of cholesterol or fats under the skin. It is often associated with high cholesterol, lipid disorders, or metabolic conditions. Genetics, age, and other factors like diabetes may also play a role.
Xanthelasma typically does not go away on its own. The plaques may remain the same size or grow over time if left untreated. Treatment is required to remove the lesions if they are a cosmetic concern or if they grow larger.
- Laser Therapy: A laser treatment that targets and removes the plaques.
- Cryotherapy (Freezing): A technique that uses extreme cold to freeze and destroy the lesions.
- Chemical Peels: The application of a chemical solution that helps in removing the plaques.
- Surgical Removal: A minor surgical procedure to cut out the lesions.
- Electrosurgery: Using electric currents to remove the plaques.
Nirvana Skin, Hair & Laser Clinic
The clinic provides a range of dermatological and hair treatments. It’s advisable to call ahead for an appointment or for more specific information about services and availability.

