
Acne Scar
Acne Scar
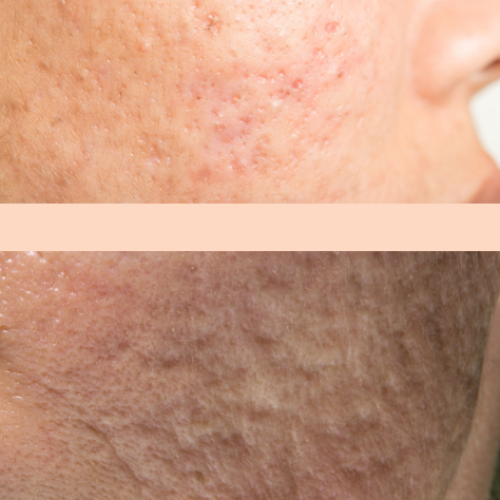
Acne scars are the marks or spots left on the skin after severe acne outbreaks or pimples heal. These scars can vary in appearance and severity, and they are often classified into different types based on their shape and depth. The most common types include:
Rolling scars: Shallow, wave-like indentations on the skin.
Ice-pick scars: Deep, narrow pits that create a sharp, narrow indentation.
Boxcar scars: Wider scars with defined, angular edges, often resembling small box-like depressions.
Treatment options for acne scars depend on the type and severity of the scars. These can range from over-the-counter creams, such as retinol, glycolic acid, or salicylic acid, to stronger prescription creams like hydroquinone or cortisone. For more severe cases, surgical treatments like dermabrasion or laser therapy may be recommended.
Acne scar treatments work to improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of scars, helping to create a smoother, more even complexion. At Nirvana Skin Hair, & Laser Clinic, our expert dermatologists assess your skin type and the extent of scarring to recommend the most suitable treatment plan tailored to your needs.
This version clarifies the different types of acne scars and treatment options while highlighting the importance of personalized care from experts.
Inflammatory Acne: Acne, particularly inflammatory acne, is one of the leading causes of acne scars. Severe types like cystic acne or nodular acne cause deeper damage to the skin, leading to scarring. When the pimples rupture beneath the surface of the skin, the surrounding tissue gets damaged, and as the wound heals, scar tissue forms.
Excessive Inflammation: When acne lesions become inflamed (red, swollen, and painful), the body produces excess collagen in an attempt to heal the skin. If too much collagen is produced, it can result in raised scars. Conversely, insufficient collagen production can lead to sunken or depressed scars, such as ice-pick or boxcar scars.
Picking or Squeezing Pimples: Picking at or squeezing acne lesions can exacerbate inflammation, pushing bacteria and oil deeper into the skin. This can increase the damage to the skin and worsen scarring. The force used in squeezing can also physically break the skin, leading to deeper tissue damage and more pronounced scars.
Delayed or Improper Acne Treatment: When acne is not treated promptly or adequately, it can become more severe and leave behind scars. Prolonged acne outbreaks, especially when left untreated, tend to heal poorly, leading to scarring.
Skin Type and Genetics: Genetics play a significant role in how the skin heals after an acne outbreak. Individuals with a family history of acne scars may be more prone to developing them. Additionally, people with darker skin tones may be more prone to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, while those with lighter skin may be more likely to develop keloid or hypertrophic scars.
Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menstruation, can increase the severity of acne, leading to more pronounced scarring. The hormonal fluctuation increases oil production in the skin, which can clog pores and result in more severe breakouts.
Raised or Thickened Skin Hypertrophic or Keloid Scars: These are raised, thickened scars that form when the skin produces too much collagen during the healing process. They often appear red, inflamed, and may be more pronounced over time.
Depressed or Sunken Areas Atrophic Scars: These scars appear as indentations or depressions in the skin, resulting from insufficient collagen production during healing. Common types include: Ice-Pick Scars: Narrow, deep pits in the skin. Boxcar Scars: Wider, angular depressions with defined edges. Rolling Scars: Shallow, wave-like indentations caused by fibrous tissue beneath the skin.
Redness or Dark Spots: After an acne lesion heals, it may leave behind a red or brown spot (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation), especially in individuals with darker skin tones. These spots can persist for weeks or months but are not true scars, as they typically fade over time.
Itching or Tenderness: Acne scars, especially those that are healing, can cause irritation, itching, or tenderness. As the skin regenerates and the scar tissue forms, this sensation may occur as part of the healing process.
Shiny or Glossy Appearance: Some types of acne scars, especially raised scars, may have a shiny or glossy appearance due to the excess collagen in the area, giving the scar a different texture from the surrounding skin.
Scarring Around Acne Lesions: Acne scars often form around previous acne lesions, including cysts, nodules, or severe pimples. They can become more prominent in areas where acne is more frequent, such as the face, back, and chest.
Improved Skin Appearance: Acne scar treatments help reduce the visibility of scars, leading to smoother, more even-toned skin. By flattening raised scars and filling in depressed scars, treatments restore a more natural skin texture and appearance.
Boosted Confidence: Acne scars, particularly those on visible areas like the face, can impact self-esteem. Effective scar treatment can help restore confidence by reducing the appearance of scars, allowing individuals to feel better about their skin.
Faster Healing: Professional treatments like laser therapy, chemical peels, or microneedling can accelerate the healing process by promoting collagen production. This leads to faster skin regeneration and a quicker reduction in scar visibility.
Targeted Treatment for Different Scar Types: Acne scars vary in shape and depth, from shallow rolling scars to deep ice-pick scars. Treatments are customized to target the specific type of acne scar you have, ensuring more effective results. Whether it’s through laser therapy, fillers, or other methods, professional care can address each type of scar more precisely.
Reduction in Pigmentation: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (dark spots) often follows acne breakouts, especially for people with darker skin tones. Acne scar treatments can also help lighten these spots and even out skin tone, leading to a more uniform complexion.
Prevention of New Scarring: Treating active acne and preventing future outbreaks is a key component of acne scar treatment. By managing current acne and preventing new breakouts, treatments can minimize the risk of developing additional scars.
Long-Lasting Results: While acne scars may not disappear completely, professional treatments offer long-lasting results. With a customized treatment plan, scar appearance can significantly improve, and the skin can continue to look smoother and healthier over time.
Frequently Ask Question
Acne scars form when the skin experiences severe acne, especially cystic or inflammatory acne. These types of acne cause deep damage to the skin, and as the body heals, collagen production can lead to scars. Factors like genetics, skin type, and improper acne treatment (such as squeezing or picking) can also contribute to scarring.
There are several types of acne scars, each with distinct features:
- Atrophic scars (depressed or sunken scars) include:
- Ice-pick scars: Deep, narrow pits.
- Boxcar scars: Broad, angular depressions.
- Rolling scars: Shallow, wave-like indentations.
- Hypertrophic scars: Raised, thick scars caused by excess collagen.
- Keloid scars: Raised, large, and often more noticeable scars that extend beyond the original injury.
While treatments can significantly reduce the appearance of acne scars, complete removal is often not possible. However, with professional care, you can achieve smoother, more even skin and a noticeable reduction in scarring, improving your skin’s overall appearance.
Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of scars:
- Topical treatments: Products with retinoids, glycolic acid, or salicylic acid.
- Chemical peels: Helps exfoliate the skin and reduce discoloration.
- Microneedling: Stimulates collagen production to reduce scar depth.
- Laser therapy: Targets deeper scars and smooths skin texture.
- Corticosteroid injections: Used to treat raised scars like hypertrophic or keloid scars.
- Dermal fillers: Used for filling in deep depressions.
The time it takes to see visible improvement depends on the treatment type and scar severity. For example:
- Topical treatments can take a few weeks to show results.
- Microneedling and chemical peels often show improvement after a few sessions.
- Laser treatments typically show noticeable results after several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the scars.
Nirvana Skin, Hair & Laser Clinic
The clinic provides a range of dermatological and hair treatments. It’s advisable to call ahead for an appointment or for more specific information about services and availability.

